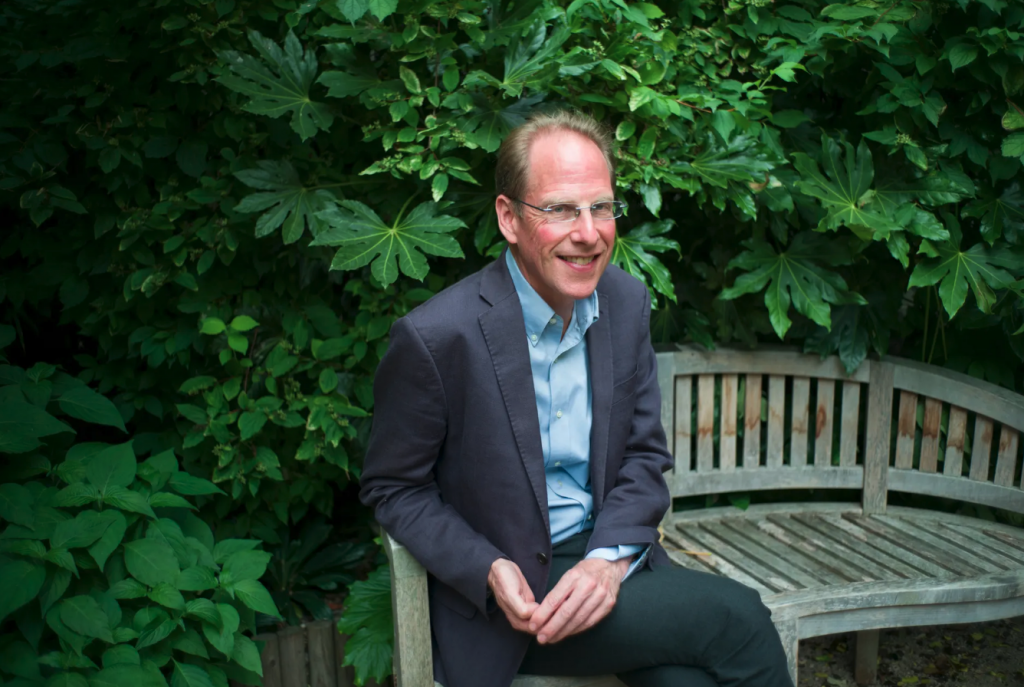
I recently interviewed Simon Baron-Cohen, a world-leading expert on autism, for the Guardian.
His latest research reflects the huge gulf between advancements in awareness and research and real, practical improvements to people’s lives.
Such findings from the Cambridge professor and director of the university’s influential Autism Research Centre add more weight to existing evidence about the significant challenges facing autistic people. Diagnosis can take years; children face cuts to special educational needs provision; just 16% of autistic people had jobs in 2016 (compared with 80% of non-autistic people); and they are among those locked up in secure hospital-style units instead of living in communities. The Autism Act a decade ago obliged the government to create a strategy to improve support, but legislation has fallen short of promises.
Baron-Cohen hopes his centre’s recent findings will encourage better practical help (a lifelong support worker, for example) “so there’s a pathway from discovery in the lab through to changing people’s lives”. This is crucial because academics are often cricitised for failing to translate knowledge into practice. A 2013 report by the charity Research Autism questioned why studies to look at effective services or to fully involve autistic people. Baron-Cohen says: “The old style of doing research was, without [us] realising it, arrogant, in that the scientists thought up the questions and then did it. The new way is to involve people from the outset… to co-design the studies and check the relevance and wording.”
I also spoke to Baron-Cohen about criticism of and controversy about some of his theories. Notably, his “extreme male brain’ concept, outlined in his provocative book, The Essential Difference. This describes men’s brains being wired for systemising and women’s for empathising. This led to criticisms of “neurosexism” and gender stereotyping which could risk misdiagnosis or under-diagnosis of autistic women.
His theories have also been challenged by autistic people who argue that they fuel the myth that they cannot empathise. Autistic academic Damian Milton, a lecturer at the Tizard Centre, University of Kent, says: “Simon’s a nice guy and knowledgeable in a lot of areas, but the empathising and sympathising theory suggests a lack of cognitive empathy, which many people in the autistic community disagree with.” Milton’s double empathy theory is a critique of Baron-Cohen’s, describing a mutual empathy problem between autistic and non-autistic people.
In response, Baron-Cohen says that with empathy “we need to make sure it’s [moving] two ways”. He stresses that while autistic people may struggle to imagine others’ emotions, they feel emotion if others are upset (the distinction between cognitive and affective empathy).
He says of criticism: “Sometimes I have to spend a lot of time explaining what it is I’m not saying…people just take the headline and think I’m saying autistic people are macho and aggressive.” Baron-Cohen stresses that “equality between the sexes is very important”, adding that his research explores groups of males and females “on average”, adding “this is not about individuals”.
You can read the piece in the Guardian here.