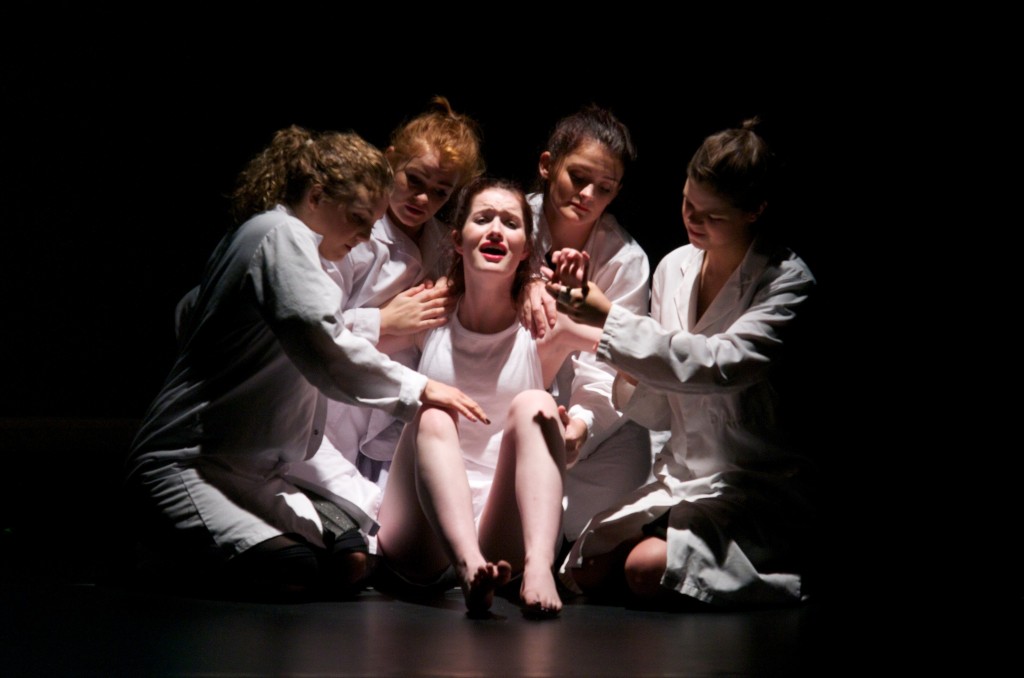
“I quite clearly remember being tied to the cot sides,” recalls Florence, now in her 70s, of the childhood she spent in hospital. “Literally, two wrists tied to the cot sides with cotton tape so as I couldn’t get up and I couldn’t sit up because they – the doctors – had decided that if there’s something wrong with your back, you have to lie prone.”
Florence’s memories are among those featured in a project that encourages schools to create theatrical performances based on real stories of disability from people born in the 1940s, 60s and 80s. The Changing Lives, Changing Times project involved workshops at three Leeds schools over five weeks last summer and led to the development of teaching packs. These help teachers run awareness-raising workshops about disability and are being sent out to UK schools by the end of the year.
The drive coincides with Disability History Month, which starts today.
The rest of my piece in the Guardian’s social care pages is here, and I’m devoting the remainder of this post to extracts from the stories of Florence and Dan, both born in the 1940s, Poppy, born in the 1960s, and Holly, born in the 1980s, reflecting the contrasting experiences of disabled people in different eras.
Florence was born in the late 1940s, the daughter of a single parent, but when doctors diagnosed that she would never walk, her birth mother left her. Florence attended mainstream schools throughout the 1950s. She left school and entered her first paid job in the mid 1960s as a telephonist and clerk. Her second job was as a typist. Florence is a trained social worker. She is single, she has no children, she drives her own car:
“There were all sorts of problems of having a child that wasn’t going to be able to get do things normally. The children’s home really wasn’t ideal and they decided that they would foster me out because there were too many kids running about in the children’s home and because I wasn’t mobile I was getting picked on, getting hit, getting spat at by the other children.
I then went to foster parents who, although they knew that I wasn’t going to be able to walk, said: “Oh yeah, we’ll manage that fine”. And they didn’t, and after two months I was back in the children’s home. The children’s home said “no, we can’t cope with her here because she’s not mobile” so I went back into hospital, where I didn’t really need to be but because there was nowhere else suitable and they couldn’t find another foster placement, so that’s where I went.
My mother still was saying, “I don’t want anything to do with this child’, which was really difficult for her because any time that I needed any surgery or any intervention they had to get hold of her, and every time I needed something obviously it brought it back to her that I wasn’t living with her. So that must have been really difficult for her.
A relative of a child that was in the next bed to me for quite a while came in and after a couple of times coming in she realised that there wasn’t anybody visiting me, because nobody from the children’s home came, my mother didn’t come, so nobody came. So she said; “Well could I still continue to visit after my niece goes home?”. And they [hospital staff] said: “Yeah if you want to”. You know: Why would you want to do this? And she said: “I just seem to have got on with her and she’s got a really nice smile”. And so after a couple of visits she’d sort of said to the nursing staff “Is there anything else I can do?” And the nursing staff had obviously said, “Well, you know, it’d be nice if you maybe spoke to the social worker”, and so they set up an appointment with the social worker – and I ended up going out to them. Initially short-term fostering and then it turned out as adoption eventually. So that was really just luck and chance.
I had absolutely no idea where I was going because there was no proprietary work done – no photograph of the house, nothing. They didn’t do things like that then, they just assumed that a child would cope with it, you know. So we ended up at this house and there were like two steps at the front door. Although they knew I couldn’t walk it just didn’t register. I suppose because they felt I could stand up, I could walk, and the two are not at all related, but to people that have not known disability … why would you think about it?
I don’t think my adoptive brother was really consulted that much about it and I think he just took the attitude, “well, I’m an adult, it’ll not bother me”. And so, because there was such a big gap there really wasn’t a very close bonding at all and there still isn’t, but there is with his children, so that’s okay.
Apparently one day when we were in the town shopping … my adoptive mother saw my other, saw my natural mother coming in the door … … and we turned and walked away. Now I have not even got any memory of what my natural mother looks like. I have nothing.”
Dan, born in the 1940s:
“I can remember, I should imagine possibly 7 or 8, being in and out of hospital and, it was suggested by the medical profession that I should go to a special school, and I always remember it was a real big old type of building and we used to be taken on a… on a blue single decker bus and this school was um, it… it was more about doing this like making raffia baskets and playing with you know, clay and they… they had gardens at the back and used to let us potter about, digging things up or planting things, but it didn’t seem to be you know, really academic type of thing, it was all about… and I always thought I was the least disabled person there to be honest.
You were sort of cotton-woolled, you went in and there was always lots of people to help you, you know go to your classroom, help you if you needed it, sitting down, people brought things to you all the time to your desk or whatever, and um, it was… you knew you was different and you had this all the time, you knew that you were, you was different from anybody else, those outside, your friends at ordinary school, you needed this particular facility because you had a disability, and it was always the physical disability that was sort of, you know, important. That’s why I’m sure you know, it was as though you were limited, your mental capacity was limited.”
Poppy, born in the 1960s, went to residential special school at the age of four until she was 16. The school became her social world and she remembers feeling bored and lonely at home during the summer holidays. Her ability to move around independently was limited by an inaccessible environment. At school there was a strict institutional regime of normalisation including intensive physio and speech therapy (“the more dependent you were, the less privileges you got”) and there was corporal punishment for non-compliance and allegations of sexual abuse from some children: “I knew it wasn’t right, but there was no one to tell”. Poppy also saw changes towards a more enlightened attitude in the late 1970’s and whilst academic expectations for the pupils were not high she was able to gain enough basic qualifications to enrol at a further education college. Here is Poppy’s story:
“My first memory of school was crawling down the corridor after my mum and dad had gone, and I was in tears, because I didn’t really understand what was happening. I never walked, I was on the floor, I always crawled, so I crawled down the corridor. So the headmistress picked me up, shouted at me and put me on my feet. They had bars on the walls, and she said ‘we don’t crawl here, we walk’ and I had to walk and I’ll never forget that. It was pretty traumatic at the time.
The school was very institutionalised, and you got up at 7 every day, including weekends, which I wasn’t too happy about, and they had set meals, you had set bath times, set bed times, the day completely structured. Luckily we did have lessons, they did try to educate you, as much as they though was possible, but I still think we had a substandard education. It wasn’t very tasking.
I remember one child getting hit around the head, and I knew it wasn’t right, but I was too scared to tell anyone.
A new headmistress came, and she had very new ideas about disabled children, and I think she had higher expectations of us, and she taught us about classical music, how to appreciate the arts, I think we responded to that quite well. We would go to the theatre or we would go on days out to the Tate Gallery.
The aim was to get us as independent as possible, but not independent to use a wheelchair to get about; you must walk, you must talk. I had speech therapy, although you couldn’t tell now. I had speech therapy, and , I had physiotherapy, and we had to dress ourselves, we had to feed ourselves, and some people weren’t able to do that; the more dependent you were, the less privileges you got. So because I could get dressed on my own, I could sneak a few minutes in bed longer in the morning, I had more freedom, you know, I could do as much as anyone, I could come and go as I pleased.
I think young people have a lot of pressure today, I think it’s harder, I know one lad, he’s at a non-disabled school and he finds it really hard to kind of be part of the whole system, because he is different, he knows he is different and in some ways, his school mates treat him differently and he hates that. I didn’t get that at school, we were all the same.
College was like a right of passage. It was where I learnt to become who I am now. The way I learnt to become, I think, an independent adult, not in the sense of learning to walk, dress and all that stuff but to think for myself, to have the choices that I wanted, and to be able to make those choices. Also it made the selection process more powerful because you knew you’d been selected because of your intelligence, and not someone patting you on the head.
I majored in English and my minor was in Sociology and we studied ethnicity, racism, and sexism, and different kinds of religions and beliefs, and age discrimination and class, nothing about disability, so at that point I wasn’t even aware I had a political identity as a disabled person.”
Holly was born, several months prematurely, in the 1980s. She was not expected to live for more than a few days and doctors advised her parents not to bond with her. Her parents separated after her impairment was diagnosed, so Holly lived with her mother, who gave up her career, and a step-brother from a previous marriage. Her mother re- married. Holly was sent to a residential special school when she was two-years-old, and stayed there until she was 18. When she left school, at the age of 18, Holly also left home, partly because she had become more distant from her parents, and because she had experienced some domestic violence and abuse. She went to a mainstream college to study dance, but never finished due to back problems. Holly lives alone in a council flat. She works as a volunteer for a local disability organization and a charity that supports children who have been abused. Holly has aspirations to do a paid job and marry her boyfriend:
“Some people are completely ignorant, not through malice but they are ignorant when it comes to disability. Somebody’s already formed in their own head what a disability means and if you kind of break their train of thought about what a disability is, you kind of completely shock them.
I think it’s changing very, very slowly but I don’t think it’s changing at the pace that it should be. I think there’s still an awful lot of undertone, tokenism, you know, people still get patronised when they’ve got a disability. I actually find the worst people for it are teenage girls – like girls in between the ages of let’s say fifteen to early twenties. I don’t know whether it’s because you know, I don’t quite understand, but I’ve experienced really quite bad attitudes with that kind of age group.
I still find it absolutely disgusting that women that need to access places like women’s refuges are turned away on the basis of their disability. I think people are still like –what do you mean domestic violence? Well, you’re disabled. Because they either think that you – that you are completely spoilt and wrapped up in cotton wool as a child, and obviously you can’t experience domestic violence from a partner because disabled people don’t have sex. I find the – worst thing a parent can do is pull a child away when they want to know why that lady is in a wheelchair. I wish to god parents would just let their children ask. And then maybe we could start educating from that age.”
Taken from Changing Lives, Changing Times, a Leeds University-led project and published with thanks to Dr Sonali Shah.