Images of churches with lepers’ squints are among hundreds included in a web-based project launched today by English Heritage. The Disability in Time and Place resource encourages the public to understand changing social attitudes to disability via England’s architecture and shows the influence of disability on the built environment.

As Rosie Sherrington, policy adviser at English Heritage says of Disability in Time and Place: “In essence we can track disabled in and out of the community and back in again by looking at the range of buildings they inhabited.”
The image-led project features institutions and landmarks, among them the Le Court Leonard Cheshire Home, often taken as the first meeting place of the disability rights movement where Paul Hunt began campaigning with other residents in care. The pictures are from English Heritage’s archive and also draw on historical images lent by the charity’s partner organisations.
Disability in Time and Place is being launched at the Graeae Theatre, Hackney (among the country’s leading fully accessible theatres) this afternoon with speakers including Tara Flood, ex-paralympian and director of ALLFIE (the Alliance for Inclusive Education), and architect and access expert Dr David Bonnett, whose pioneering work includes the refurbishment of the Royal Festival Hall.

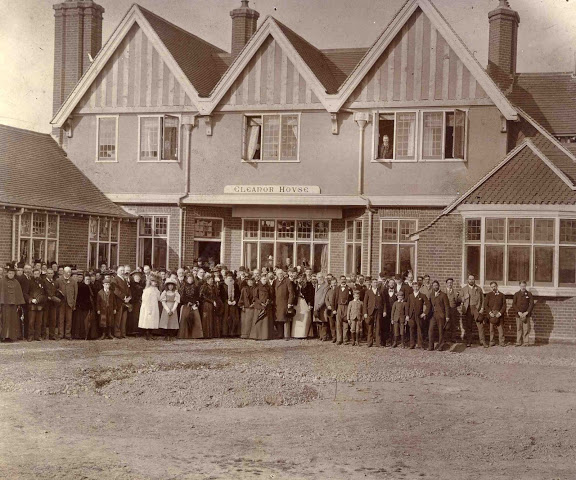
Among the places featured is the Guild of Brave Poor Things in Bristol (above), the first meeting places for disabled self-help groups. The visual history also includes the Liverpool School for Indigent Blind, opened in 1791 by Edward Rushton, who was blind. Rushton’s school was the first in Britain that aimed to give people the skills to be more independent.
Other sites featured are churches designed for deaf congregations such as St Bede’s Church in Clapham and St Saviour’s in Acton, both in London (the latter is still used as a deaf church). They have dual pulpits, one for the chaplain and one for the interpreter, as well as bright lighting and raked seating to boost visibility.
English Heritage’s web resource is divided into six sections, each taking a specific historical period – the Tudors or the early 20th century, for example – and looks at the building types associated with it.
Sherrington adds: “In the medieval period we have the idea that disability was a direct consequence of mankind’s sin, and therefore a religious matter. However disability as a result of disease such as leprosy was widespread, and an ordinary part of everyday life. It was not understood in the same way as we see it today.”
Moving onto Tudor times, she says, much of the care provided by monasteries and the church was destroyed during the dissolution, having disastrous consequences on the lives of disabled people. Paradoxically, Henry VIIIs “fools” were people with learning disabilities paid to entertain the court. It was a privileged role and they were thought to have divine wisdom.
“The 18th century saw the idea of disability being a matter of physicality rather than morality,” according to Sherrington, “and providing for the disabled became a matter of civic pride. As such many private asylums and enormous hospitals for the war disabled (like the Chelsea Pensioners) were built.”
With the rise of asylums and workhouses, disabled people were hidden away (although Sherrington adds “ this was though of as a positive move enabling disabled people to receive the ‘treatment’ they needed”). With the 20th century came the attitude that many people had incurable conditions (Sherrington draws our attention to the rise of eugenics “and the perceived need to separate those who were ‘healthy’ from those believed to be ‘inferior’”). But then two World Wars resulted in the notion of “heroic disabled” and the emergence of memorial villages and specialist rehabilitation hospitals.
According to Baroness Andrews, who chairs English Heritage, the project “is a history of the nation’s buildings and of a significant proportion of our population which, until now, has gone unexamined and untold. It is the part of the history of every town and city, with the schools, chapels and hospitals which surround us all each day but it has remained invisible and silent.”
English Heritage worked with a disability history steering group which included disabled employees, disability history academics including Jan Walmsley from the Open University’s Social History of Learning Disability Group and Dr Julie Anderson from the University of Kent who specialises in war disability. Partners included ALLFIE (the Alliance for Inclusive Education). Other sources of advice, information and images include the Greater Manchester Coalition of Disabled People, Disability History Month, the Centre for Disability Studies in Leeds, Leonard Cheshire, the Epilepsy Society, New College Worcester. All the content has been translated into British sign language videos by deaf interpreters.
* English Heritage has also updated its, Easy Access to Historic Buildings, available to download.